
Pxfuel
Extreme weather has been the cause of some of the biggest public health crises across the world in recent years. In many cases, these have been enhanced by human-induced climate change. For instance, in 2003, high summer temperatures in Europe were believed to cause 50,000 to 70,000 excess deaths across 16 European countries.
Globally, it’s been estimated that a total of 296,000 deaths over the past two decades have been related to heat.
But heat doesn’t just affect physical health. It can have equally serious effects on mental health conditions. Research has shown that rising temperatures are associated with an increase in suicides and in violent behaviour, as well as exacerbating mood and anxiety disorders.
Studies in England and Wales conducted between 1993 and 2003 have revealed that, when temperatures were above 18°C, every 1°C rise in temperature was associated with a 3.8% increased risk of suicide across the population.
Between 1996 and 2013 in Finland, every 1°C increase in temperature accounted for a 1.7% increase in violent crime across the country. It has even been estimated that 1.2 million more assaults might occur in the United States between 2010 to 2099 than would without climate change.
The association between high temperatures and mental health is an active area of research. Scientists have found that some health consequences of increased heat, like disturbed sleep and levels of serotonin – a hormone critical for adjusting our feelings, emotions and behaviours – might play a role in triggering the appearance of mental health conditions.
Author provided
Sleep deprivation often occurs during heatwaves, which then may lead to frustration, irritability, impulsive behaviours and even violence.
Extreme temperatures, such as those observed during heatwaves, are also found to be associated with some forms of dementia and disturbed mental health states, especially for those who are already in vulnerable conditions such as psychiatric patients.
And low levels of serotonin are associated with depression, anxiety, impulsivity, aggression and occurrence of violent incidents.
Implications
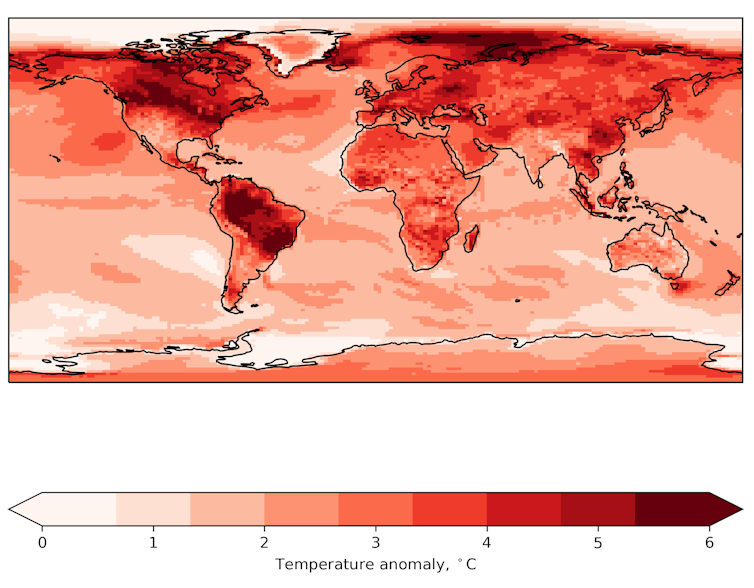
In the future, heatwaves will be hotter and last longer. Temperature records are likely to be broken ever more frequently as the world continues to warm. In north-west Asia, for example, temperatures could increase by 8.4°C by 2100.
A world that is on average 1.5°C warmer will see many average regional temperatures rise by more than this. This problem is compounded as the population – and therefore the number of people living in cities – increases. By 2050, it is projected that two thirds of the world’s population will live in urban areas.

PedroFigueras/Pixabay
Urban environments are known to be warmer than their rural surroundings, a phenomenon known as the “urban heat island”. Climate projections show not only that cities will warm faster than rural areas, but that this effect is increased at night. This may further exacerbate the effects of heat extremes on our sleep.
Both adaptation to and mitigation of climate change will be necessary to lessen these potentially devastating effects as much as possible.
Options for adapting our lives to a warmer world could include increasing air circulation within buildings and adjusted work hours in times of extreme heat. Paris, for example, has already created a network of “cool islands”: green and blue spaces such as parks, ponds and swimming pools which provide places to seek refuge from the heat.
Most simply, educating people on the potential impacts of heat on mental health, aggression and violence – allowing them to understand exactly why it is so important to support initiatives that help keep our planet cool – could support better mental health at the same time as fighting the climate crisis.
—————————————–![]()
This blog is written by Cabot Institute for the Environment members Dr Mary Zhang, Senior Research Associate in Policy Studies, University of Bristol; Professor Dann Mitchell, Associate Professor in Atmospheric Sciences, University of Bristol, and Dr Vikki Thompson, Senior Research Associate in Geographical Sciences, University of Bristol
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
 |
| Dann Mitchell |
 |
| Mary Zhang |
 |
| Vikki Thompson |
Read all blogs in our COP26 blog series:

