In October and November 2019 Caboteer Dr Lauren Blake spent time in Boyacá, Colombia, on a six-week fieldtrip to find out about key socio-environmental conflicts and the impacts on the inhabitants of the páramos, as part of the historical and cultural component of her research project, POR EL Páramo. Background information about the research can be found in the earlier blog on the project website.
Descending down the hill in the bus from El Crucero, the pungent smell of cebolla larga onion begins to invade my nose. The surrounding land transforms into plots of uniform rows of onion tops at various stages of growth, some mostly brown soil with shoots poking out along the ridges, others long, bushy and green. Sandwiched between the cloud settled atop the mountainous páramos and the vast, dark blue-green Lake Tota, all I can see and all I can smell is onion production. Sprinklers are scattered around, drawing water from the lake, and large teams of labourers every few plots harvest en-masse. Some may see this as a bucolic landscape, indeed, there are ‘ecotourism’ posters advertising ‘agroturismo’ tours to learn about cebolla larga production. However, there is a less romantic idyllic side to this industry, which Aquitania and the surrounding area depend on heavily: around 90% of Aquitanenses’ economic activity is related to the onion industry.
 |
| Approaching Aquitania, where onion cultivation start to dominate the surroundings. Image credit: Lauren Blake. |
Aquitania lies at an altitude of 3,030 meters, that is, 30 meters above the supposed line where páramo land begins, according to the Humboldt Institute. As such, this intense onion cultivation would be in breach of the delimitation law (Ley 1930 of 2018) that wants to limit agricultural activities because of their damaging effects on páramo ecosystems, which are now the focus of intense conservation efforts. The area under cultivation immediately around the lake was omitted in the delimitation (around 95% of the cultivable land in the water basin is under cebolla production), perhaps due to the economic importance of the onion industry and maybe even some pressure from the influential landowners who benefit from it. Indeed, many livelihoods depend on cebolla there, so it is complicated. The fieldtrip was aimed at understanding the tensions between livelihoods and conservation at different points of the Boyacá páramos, so Aquitania was an interesting place to start.
 |
| From a viewpoint higher up in the páramos, looking down over the town of Aquitania. The cebolla production expands all around it and reaches right upto Lake Tota. Image credit: Lauren Blake. |
Cultivation of cebolla larga (picture a spring onion the size of a leek, also known as cebolla junca and cebolla de rama) began in the 1960s, following the demise of wheat, barley and a range of cold-weather crops, and the encouragement for specialisation and intensification (Galli 1981, Instituto Humboldt 2014) – evidenced in the diminished local weekly market. Since then, cebolla larga farming has grown exponentially: there are approximately 1,300 hectares under onion production around Aquitania (some estimate as much as 2,500, especially when the whole municipality is counted), where upwards of 500 tonnes are harvested per day – 200,000 tonnes annually, dominating over 80% of the national market and providing cebolla larga all over Colombia. Toxicologists are worried about the use of chemical fungicides, herbicides and pesticides which growers deem essential, as well as high amounts of gallinaza (chicken manure) for fertilizer, the quantities of each which are only ever increasing as land tires, diseases and insects become resistant, and pressure on yield dominates. Scientists from the UPTC (Universidad Pedagógica y Tecnológica de Colombia) are concerned about the toxicity of the lake, which receives the run-off, as indicated by emerging toxicology studies (Barrera, Espinosa-Ramírez and Silva 2019). Growing virtually nothing else, with year-round production and 3-4 harvests annually, Aquitania is the epicentre of the cebolla larga industry and is where producers, intermediaries and distributors are concentrated. Famous for its production, onion has come to form an integral part of the Aquitanense identity, and there are calls for Protected Designation of Origen (like champagne or roquefort cheese). In the central plaza amidst a water fountain, the most prominent feature is a statue of a man standing on top of a giant bunch of cebolla larga, harvesting tool across his shoulder, onions clutched in his hand. This proud identity is reflected again in a nearby mural depicting an image of cebolla larga alongside a statement on being Aquitanense (“Soy Cultura, Soy Ambiente, Soy Aquitanense”: “I am culture, I am environment, I am Aquitanian”).
 |
| Mural about Aquitanense identity and water fountain in the central plaza depicting onions and onion producers. Image credit: Lauren Blake. |
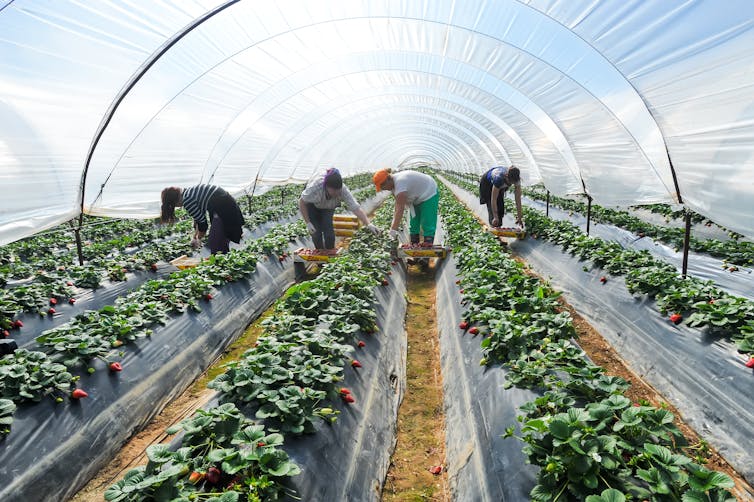
The Aquitanenses I encountered were incredibly kind and open in sharing their lives with me. I spent time with campesinos who live above the town and benefit only marginally from onion production – with limited access to irrigation away from the lake, fewer resources to input, smaller plots of land and within the protected delimited páramos. I also spent time with jornaleros/cebolleros – day labourers who plant, weed, fumigate and harvest the crop –, and in a pelanza de cebolla – a processing operation where the onions are peeled and packed into nets of 500g and 1kg bunches, largely for direct sale in Bogotá supermarkets. The pelanza takes place in simple warehouses which employ mostly women – with male bosses and managers – who are paid by the quantity of bunches they process. The rectangular warehouse I spent time in was a closed space with a surprisingly low ceiling, one opening on the narrow side with no other windows, a few skylights for visibility, concrete block walls, corrugated fibreglass roof and dirt floor, making the conditions stuffy and dingy for the 15-20 or so workers inside. Throughout the day, the women have with them their babies and infants, who nap and play amongst piles of onions; their older children join after school. It is grubby, hard work, and it didn’t take long before my eyes and nose were irritated and streaming, with a headache lingering well into the night. I wondered if there were residues from the multiple chemical applications, and if this affected the health of the women and their children in the poorly ventilated space. They were concerned, but grateful to have work. I was full of admiration and compassion for them. They were understandably a little suspicious of me at first, but warm, curious and increasingly welcoming, especially once I had learned how to peel adequately!
 |
| A ‘pelanza’ where women process the onion ready for supermarket shelves. Image credit: Lauren Blake. |
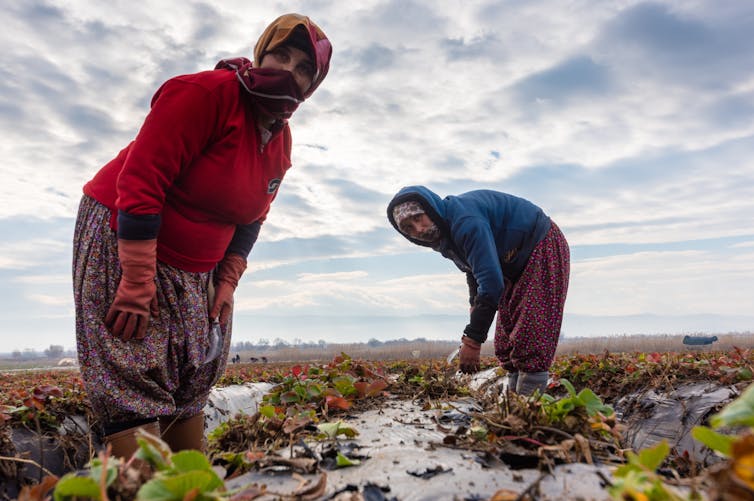
Out in the fields with the jornaleros, I imagined, or rather hoped, the open air would minimise the irritation to my sinuses, but I still felt the aroma permeate my eyes and respiratory system. The work, demanding constant bending over and, for the men, heavy lifting and carrying, is quite literally back breaking. The men are out from about 5am until late lunch, with female partners/family members joining them after taking children to school (and whenever school is closed, children help too, to learn working skills). Cebolla larga generates employment for 170 jornaleros (daily labourers) per hectare per day (Acevedo 2018) and since 89% of the land is occupied by only 20% of the population, in contrast to the 81% of land owners with less than 3 hectare plots (Albarracín 2015), most of Aquitania men are contracted on a daily basis. Hence, whilst there’s often work, there’s little security, and certainly no benefits like sick pay, healthcare, or pensions. The labour is arranged directly with men and the wage goes directly to the man, usually the day before, so whilst female family members work alongside them most of the time, they do not receive a wage. At 50,000 Colombian Pesos a day (about £10), whilst high compared to some manual labour work in Colombia, it is not well remunerated, especially when the man is accompanied by female family members (and sometimes children), which increases the amount of labour for the wage. Working 6, sometimes 7, days a week, most of the jornaleros have spent their entire lives in this work since childhood and see little difference for their future. There is an interesting tension. On the one hand, they feel “solo” (alone), with little state and welfare support, not unionised, and they see few alternatives for the rest of their lives, which can be depressing. On the other hand, they are proud, hard workers and grateful to be in a place with such reliable employment: “those who go hungry are those who do not want to work, because here we’re blessed with plenty of work” – variations of this comment were commonplace. However, it comes at a cost to the social fabric. Several interviewees reported that the rates of alcoholism, especially amongst men and linked to high levels of domestic violence, are amongst the highest in Boyacá.
 |
| Labourers load up the trucks for Bogota having harvested the onion. Image credit: Lauren Blake. |
The jornaleros are concerned about their health – they know more than most how much chemical inputs are used in the onion production. However, similarly to the women in the pelanza, they are glad that the lake cultivation area is not included in the páramo delimitation, therefore meaning their livelihoods are protected. Indeed, despite being above the 3,000 meters mark, the lack of the characteristic frailejones around the lake indicate to them that they are not in páramo land, which they say is “más arriba” (further up). Having said that, the mounting environmental concerns of the production and increasing pressure to address them prompted from the delimitation debates do worry them – what employment will Aquitanenses have if the cebolla industry is restricted? The landowners and the representatives of the cebolla larga industry seem to have similar concerns and have been heavily active in their opposition to the delimitation and any environmental restrictions. NGOs and public officials in the area have reported that landowners and employers in the industry, who have had a free reign for decades, have demonised them by fuelling fears that the authorities and environmentalists want to stop the production and take away the various jobs (see also studies on socio-environmental conflicts around Aquitania such as Instituto Humboldt 2014 and Carrasco 2018).
 |
| A campesina milks her cow in the paramos above Aquitania and Lake Tota. Image credit: Lauren Blake. |
In contrast to the Lake Tota industrialised economy, above the town, campesinos have been pushed further up into the páramos and pushed out of their small holdings. They try to participate in the onion industry on marginal land; many have given up and abandoned their dwellings, moving down to Aquitania to work as a labourer, joined the transport business integral to the industry, or migrated further afield to larger urban centres in search of better paid and less back-breaking work. Those who have stayed struggle to compete with the industrial level of production below, but have little choice, as there’s scant market aside from cebolla larga in the area. As a result, it is common to see cultivation right up to the edges of roads and buildings. Women from the Association of Female Campesinas (ASOMUC) report that male household heads are reluctant to allow them to use even small amounts of land to diversify their production, income and family food supply; for the men, every square meter should be onions. Whilst most other crops fetch a poor price at market, like in many other parts of Boyacá and Colombia, milk is one of the commodities that provides a dependable income, even at a small scale. With every inch taken up by onion, cows (often around 2 per household) are found grazing the verges between plots and taken higher up in the páramos above cultivation. Despite this, Aquitania is one of the few municipalities that has no milk collection service for the veredas (hamlets), making it difficult to sell surplus – all the infrastructure focus is on cebolla. Overall, the campesinos I spoke to were angry and felt betrayed and neglected by the government, who provide little support and instead are felt to mainly impose restrictions. Already struggling to survive and maintain their livelihoods, they feel disadvantaged and cut off from the participation and benefits of the onion industry and market, whilst any other activities are not supported either. Furthermore, they now fear the implications of living in and depending on delimited páramo land, worried that the government and authorities will soon prohibit them from practicing the marginal cultivation and livestock that they rely on. Feeling abandoned, the campesinos are often driven to abandon their smallholdings.
 |
| Abandoned house with onion planted right up to the edges. Image credit: Lauren Blake. |
——————————————————
 |
| Dr Lauren Blake |