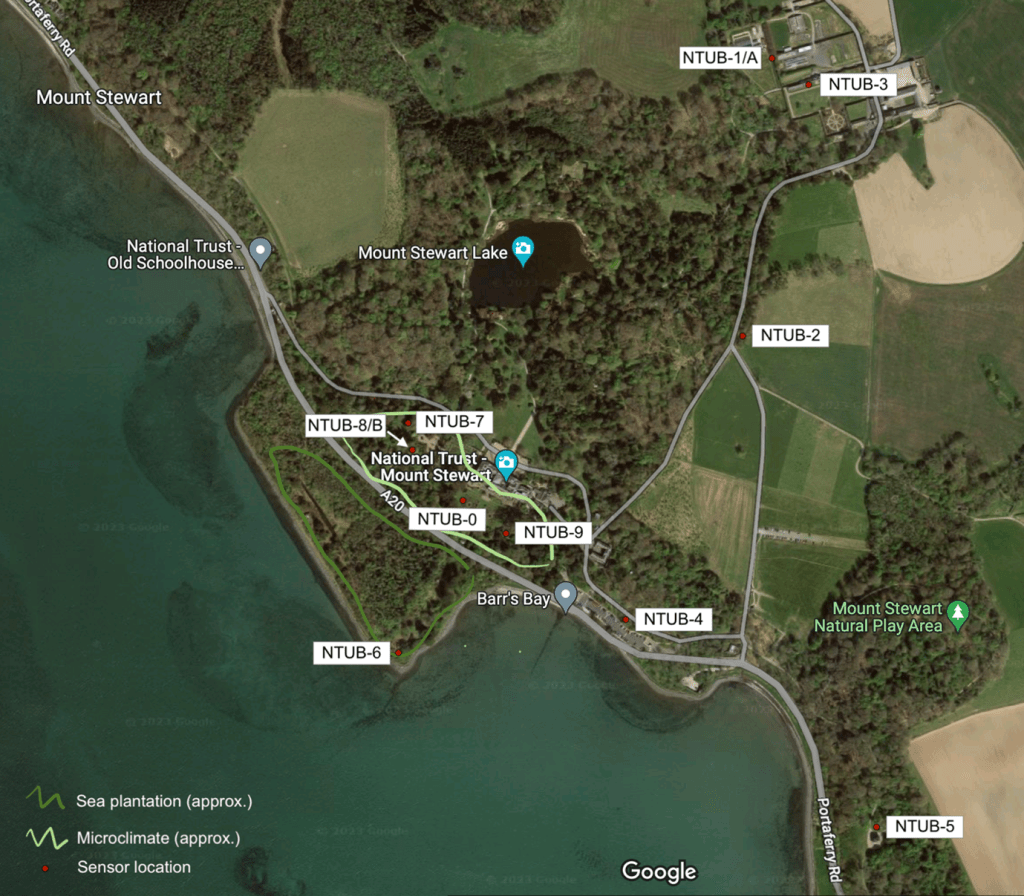
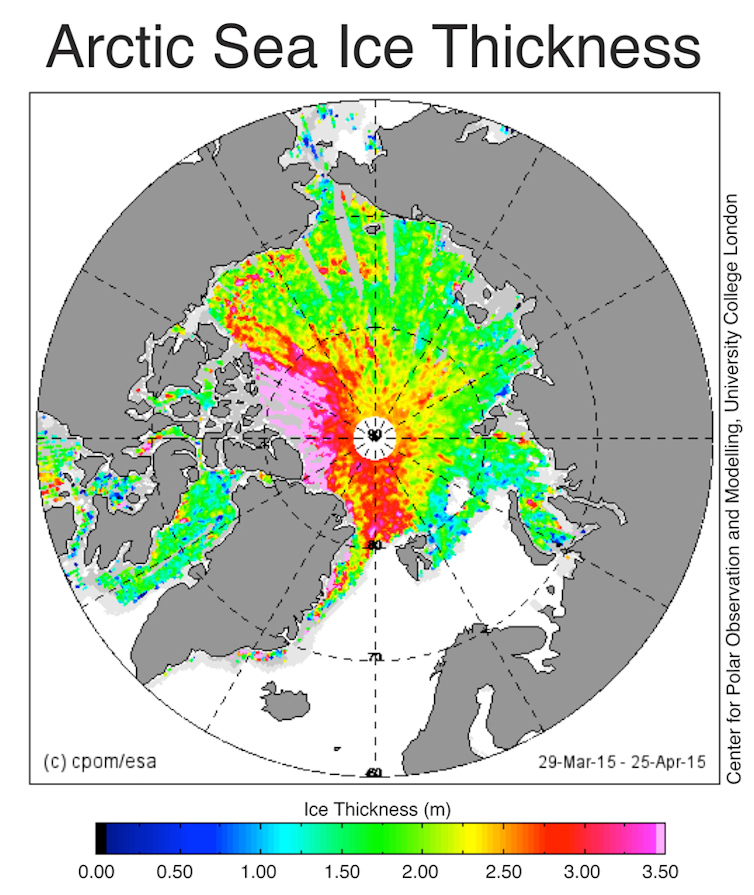
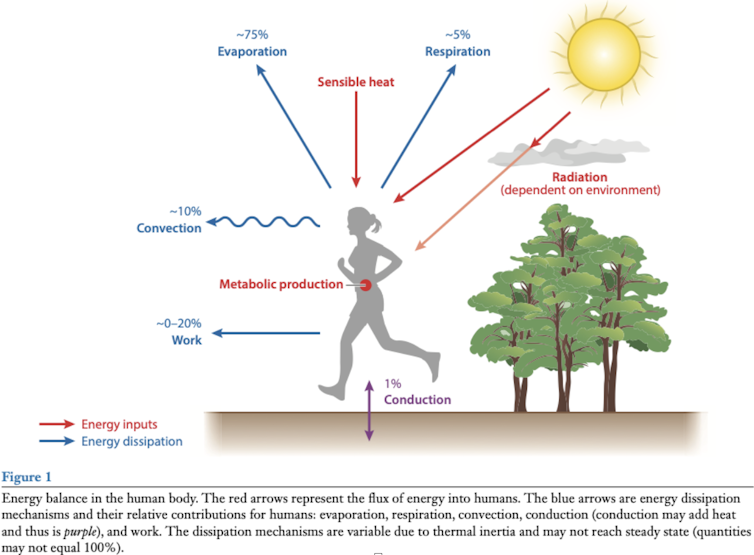
We’ve got lots of media trained climate change experts. If you need an expert for an interview, here is a list of our experts you can approach. All media enquiries should be made via Victoria Tagg, our dedicated Media and PR Manager at the University of Bristol.
Email victoria.tagg@bristol.ac.uk or call +44 (0)117 428 2489.
Climate change / climate emergency / climate science / climate-induced disasters
Dr Eunice Lo – expert in changes in extreme weather events such as heatwaves and cold spells, and how these changes translate to negative health outcomes including illnesses and deaths. Follow on Twitter/X @EuniceLoClimate.
Professor Daniela Schmidt – expert in the causes and effects of climate change on marine systems. Dani is also a Lead Author on the IPCC reports.
Dr Katerina Michalides – expert in drylands, drought and desertification and helping East African rural communities to adapt to droughts and future climate change. Follow on Twitter/X @_kmichaelides.
Professor Dann Mitchell – expert in how climate change alters the atmospheric circulation, extreme events, and impacts on human health. Dann is also a Met Office Chair. Follow on Twitter/X @ClimateDann.
Professor Dan Lunt – expert on past climate change, with a focus on understanding how and why climate has changed in the past and what we can learn about the future from the past. Dan is also a Lead Author on IPCC AR6. Follow on Twitter/X @ClimateSamwell.
Professor Jonathan Bamber – expert on the impact of melting land ice on sea level rise (SLR) and the response of the ocean to changes in freshwater forcing. Follow on Twitter/X @jlbamber
Professor Paul Bates CBE – expert in the science of flooding, risk and reducing threats to life and economic losses worldwide. Follow on Twitter/X @paul_d_bates
Dr Matt Palmer – expert in sea level and ocean heat content at the Met Office Hadley Centre and University of Bristol. Follow on Twitter/X @mpclimate.
Professor Guy Howard – expertise in building resilience and supporting adaptation in water systems, sanitation, health care facilities, and housing. Expert in wider infrastructure resilience assessment.
Net Zero / Energy / Renewables
Dr Caitlin Robinson – expert on energy poverty and energy justice and also in mapping ambient vulnerabilities in UK cities. Caitlin will be virtually attending COP28. Follow on Twitter/X @CaitHRobin.
Professor Philip Taylor – Expert in net zero, energy systems, energy storage, utilities, electric power distribution. Also Pro-Vice Chancellor at the University of Bristol. Follow on Twitter/X @rolyatlihp.
Dr Colin Nolden – expert in sustainable energy policy, regulation and business models and interactions with secondary markets such as carbon markets and other sectors such as mobility. Colin will be in attendance in the Blue Zone at COP28 during week 2.
Professor Charl Faul – expert in novel functional materials for sustainable energy applications e.g. in CO2 capture and conversion and energy storage devices. Follow on Twitter/X @Charl_FJ_Faul.
Climate finance / Loss and damage
Dr Rachel James – Expert in climate finance, damage, loss and decision making. Also has expertise in African climate systems and contemporary and future climate change. Follow on Twitter/X @_RachelJames.
Dr Katharina Richter – expert in decolonial environmental politics and equitable development in times of climate crises. Also an expert on degrowth and Buen Vivir, two alternatives to growth-based development from the Global North and South. Katarina will be virtually attending COP28. @DrKatRichter.
Climate justice
Dr Alix Dietzel – climate justice and climate policy expert. Focusing on the global and local scale and interested in how just the response to climate change is and how we can ensure a just transition. Alix will be in attendance in the Blue Zone at COP28 during week 1. Follow on Twitter/X @alixdietzel.
Dr Ed Atkins – expert on environmental and energy policy, politics and governance and how they must be equitable and inclusive. Also interested in local politics of climate change policies and energy generation and consumption. Follow on Twitter/X @edatkins_.
Dr Karen Tucker – expert on colonial politics of knowledge that shape encounters with indigenous knowledges, bodies and natures, and the decolonial practices that can reveal and remake them. Karen will be in attending the Blue Zone of COP28 in week 2.
Climate change and health
Dr Dan O’Hare – expert in climate anxiety and educational psychologist. Follow on Twitter/X @edpsydan.
Professor Dann Mitchell – expert in how climate change alters the atmospheric circulation, extreme events, and impacts on human health. Dann is also a Met Office Chair. Follow on Twitter/X @ClimateDann.
Dr Eunice Lo – expert in changes in extreme weather events such as heatwaves and cold spells, and how these changes translate to negative health outcomes including illnesses and deaths. Follow on Twitter/X @EuniceLoClimate.
Professor Guy Howard – expert in influence of climate change on infectious water-related disease, including waterborne disease and vector-borne disease.
Professor Rachael Gooberman-Hill – expert in health research, including long-term health conditions and design of ways to support and improve health. @EBIBristol (this account is only monitored in office hours).
Youth, children, education and skills
Dr Dan O’Hare – expert in climate anxiety in children and educational psychologist. Follow on Twitter/X @edpsydan.
Dr Camilla Morelli – expert in how children and young people imagine the future, asking what are the key challenges they face towards the adulthoods they desire and implementing impact strategies to make these desires attainable. Follow on Twitter/X @DrCamiMorelli.
Dr Helen Thomas-Hughes – expert in engaging, empowering, and inspiring diverse student bodies as collaborative environmental change makers. Also Lead of the Cabot Institute’s MScR in Global Environmental Challenges. Follow on Twitter/X @Researchhelen.
Professor Daniela Schmidt – expert in the causes and effects of climate change on marine systems. Dani is also a Lead Author on the IPCC reports. Also part of the Waves of Change project with Dr Camilla Morelli, looking at the intersection of social, economic and climatic impacts on young people’s lives and futures around the world.
Climate activism / Extinction Rebellion
Dr Oscar Berglund – expert on climate change activism and particularly Extinction Rebellion (XR) and the use of civil disobedience. Follow on Twitter @berglund_oscar.
Land / Nature / Food
Dr Jo House – expert on land and climate interactions, including emissions of carbon dioxide from land use change (e.g. deforestation), climate mitigation potential from the land (e.g. afforestation, bioenergy), and implications of science for policy. Previously Government Office for Science’s Head of Climate Advice. Follow on Twitter @Drjohouse.
Professor Steve Simpson – expert marine biology and fish ecology, with particular interests in the behaviour of coral reef fishes, bioacoustics, effects of climate change on marine ecosystems, conservation and management. Follow on Twitter/X @DrSteveSimpson.
Dr Taro Takahashi – expert on farming, livestock production systems as well as programme evaluation and general equilibrium modelling of pasture and livestock-based economies.
Dr Maria Paula Escobar-Tello – expert on tensions and intersections between livestock farming and the environment.
Air pollution / Greenhouse gases
Dr Aoife Grant – expert in greenhouse gases and methane. Set up a monitoring station at Glasgow for COP26 to record emissions.
Professor Matt Rigby – expert on sources and sinks of greenhouse gases and ozone depleting substances. Follow on Twitter @TheOtherMRigby.
Professor Guy Howard – expert in contribution of waste and wastewater systems to methane emissions in low- and middle-income countries
Plastic and the environment
Dr Charlotte Lloyd – expert on the fate of chemicals in the terrestrial environment, including plastics, bioplastics and agricultural wastes. Follow on Twitter @DrCharlLloyd.
Cabot Institute for the Environment at COP28
We will have three media trained academics in attendance at the Blue Zone at COP28. These are: Dr Alix Dietzel (week 1), Dr Colin Nolden (week 2) and Dr Karen Tucker (week 2). We will also have two academics attending virtually: Dr Caitlin Robinson and Dr Katharina Richter.
Read more about COP on our website at https://bristol.ac.uk/cabot/what-we-do/projects/cop/
——————————
This blog was written by Amanda Woodman-Hardy, Communications and Engagement Officer at the Cabot Institute for the Environment. Follow on Twitter @Enviro_Mand and @cabotinstitute.
Watch our Cabot Conversations – 10 conversations between 2 experts on a climate change issue, all whilst an artist listens in the background and interprets the conversation into a beautiful piece of art in real time. Find out more at bristol.ac.uk/cabot/conversations.
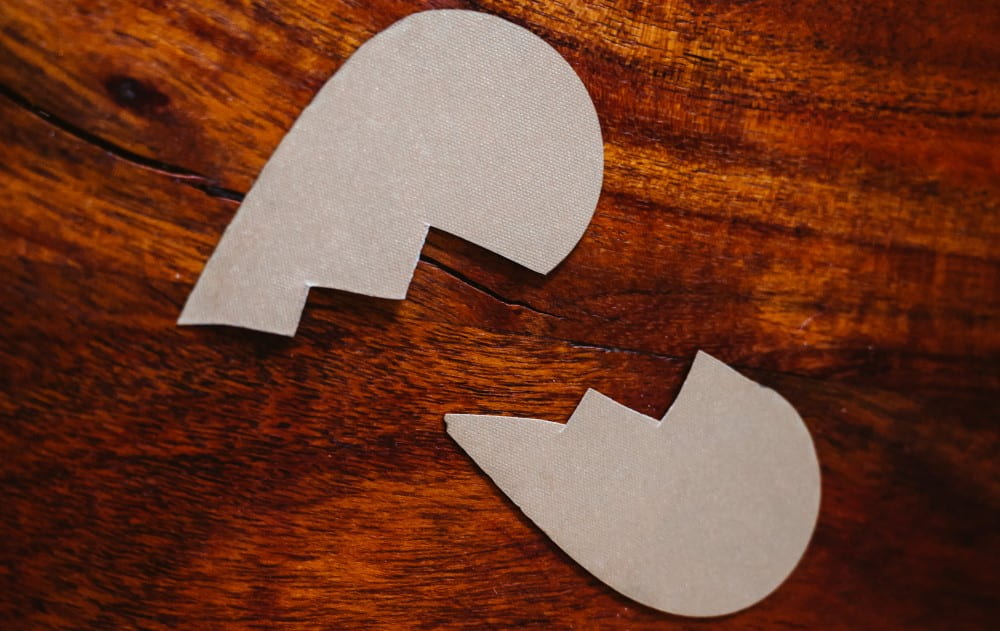
 In an ever-evolving world, societal dynamics are continually shifting, reflecting the multifaceted nature of the human experience. One of the most profound changes we have witnessed in recent decades is the transformation of family structures, with divorce becoming a common facet of modern life
In an ever-evolving world, societal dynamics are continually shifting, reflecting the multifaceted nature of the human experience. One of the most profound changes we have witnessed in recent decades is the transformation of family structures, with divorce becoming a common facet of modern life