Glasgow COP26 presentation, preliminary discussion, and negotiation rounds 1 & 2
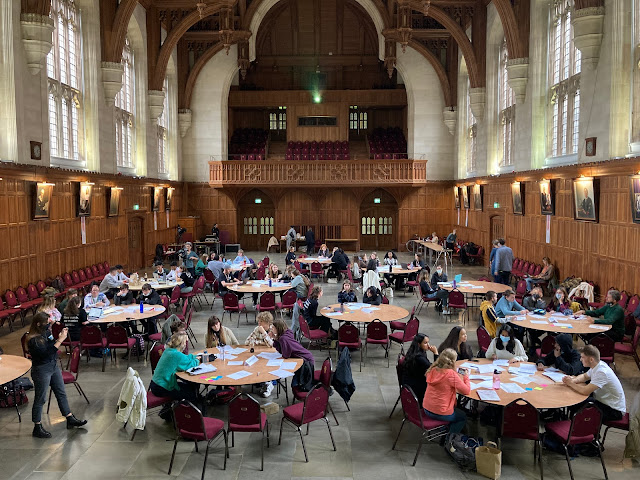
On 11th November at 10am around 60 A-level students from schools across Bristol gathered to participate in this year’s Mock COP26, hosted by Jack Nicholls, Emilia Melville, and Camille Straatman from the Cabot Institute for the Environment. After a resounding success from the first Mock COP, which took place online in March 2021, there was real excitement and anticipation building for the in-person event which would be held in the Great Hall of the Wills Memorial Building.
The morning kicked off with an engaging presentation by Jack, Emilia, and Camille, outlining the objectives of the upcoming COP26 in Glasgow. There had been much discussion surrounding the COP in the public sphere in the prior weeks, so it was interesting to see a summary of where things stand in the time since the Paris Agreement and what the potential outcomes of this COP may be.
The negotiations began with preliminary intra-group discussions, facilitated by a group of 12 postgraduate students. Each group defined their stance on each of the COP resolutions, ranging from option A, the most radical response, to C, the most conservative. It was evident from the off that these students were highly knowledgeable and passionate about the environmental, sociological, and economic impacts of each resolution, and as a result, each group wasted no time in prioritising the resolutions that would benefit their actor the most. Brazil factored in its current economic and development situation, as well as the Amazon’s critical role in the ecosystem balance, choosing to prioritise climate finance, natural protection and conservation and protecting climate refugees. For the International Indigenous Peoples Forum on Climate Change (IIFPCC), giving protected status to 50% of Earth’s natural areas by 2050 was defined as the most important resolution, whereas Shell chose to focus on phasing out coal, with the understanding that this would take the onus off the oil industry. Each group presented their ideal resolutions in a clear and concise manner.
The atmosphere really started to build in the hall when the first round of negotiations began. China faced Greenpeace in a heated discussion on coal usage while the IIFPCC negotiated with the USA on protecting indigenous populations. The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees found alignment with Brazil on many of the resolutions, namely achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, natural protection and conservation to 30% of Earth’s natural areas and protecting climate refugees. In round two of negotiations, we saw Shell and the International Monetary Fund categorically disagree on the timeline for transition to Zero Emissions Vehicles, eventually compromising on a B resolution to have all new vehicle sales as zero-emission by 2040. Brazil was happy in supporting the IIPFCC in resolution 7a. (All countries must allow people fleeing from natural disasters, environmental degradation, and sea level rise to enter their countries and make their new homes there). Brazil and IIPFCC made an alliance to encourage USA toward resolution 7a, instead of their preferred 7b (Countries at risk of extinction from sea level rise should be provided with new land to settle and move their people to OR be provided with financial help to buy land in other nations). China and the Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS) clash on coal usage, with AOSIS pushing back with a suggestion of image control, but ultimately China held strong on their decision.
Negotiation rounds 3 & 4, voting, and deputy mayor’s speech
The UK showed their tactical abilities and their knowledge in the negotiations with Greenpeace, but Greenpeace did not cede to their demands and manage to agree to a deal. The IIPFCC was determined to protect indigenous land and communities, but their quest was heavily challenged by Shell. There was no common ground in the negotiation with this petrol giant, so the IIPFCC had to ensure an allyship with Brazil if they wanted to ensure the protection of the indigenous. On round four, Shell tried to sway some votes from China and Sweden, but while agreements were found with the former, the latter country was not going to let Shell influence their values. The tête-à-tête became lively as neither Shell nor Sweden were willing to compromise, resulting in a rather unsuccessful attempt of finding complicity.
After four intense rounds of negotiating, the voting began. Were all parties going to remain faithful to the agreements established during the negotiations? Or would some throw a curve ball, changing their minds at the last minute? The pondered tactics of the IIPFCC were successful, as they managed to lock Brazil’s and the USA’s support on their most valued resolutions. All parties pondered thoroughly on how to best use their votes, and it seemed that this meant that some agreements had been silently retracted, when some astonished reactions followed the raise of hands here and there.
The conference was finally over and many parties, including Brazil and Greenpeace, could celebrate the victory of the resolutions agreed upon. Yet, it was clear that a bittersweet aftertaste was left in the mouths of some parties, who did not manage to persuade enough. The heated debate had ended, and what was done was done, but one more surprise was awaiting our participants. Deputy Mayor Asher Craig had been sitting on the sidelines for a few instances already, assisting in the final yet most heated rounds of the conference. She was there, observing our pupils in awe as they got into character and avidly fought for their beliefs. The Deputy Mayor was impressed by the passion of these young minds and how much they are invested in the cause; she was proud to see that young generations care about the environment and our planet, as they came up with ideas for change that they would like to see more in the Bristol. The innovativeness and creativity of the students was remarkable in her eyes, as she proceeded to give an inspiring and uplifting speech on the efforts currently being made by the City Council to respond to the climate emergency. The mock COP26 was a more than a successful event, and as everyone waited for the results of the conference in Glasgow, we all wished that our simulation had been real.
Watch the students in action in this short video created by Particle Productions and funded by Bristol City Council.
————————————–
This blog is written by Sonia Pighini and Jennifer Malone, who are students on the Cabot Institute for the Environment Master’s by Research.
 |
| Jennifer Malone |
.jpg) |
| Sonia Pigini |
Sonia is an international student in the MscR programme Global Environmental Challenges. Their research focuses on people-centred sustainable food system transitions in Bristol. They are particularly interested in exploring the potential for a more decentralised food system in the city, which empowers local producers, engages consumers and that keeps aspects such as justice and inclusion at its heart.
Image credit (image at top of blog): Jack Pitts