The Cabot Institute for the Environment sent three delegates to the recent Conference of the Parties 27 (COP27). Drs Alix Dietzel (Sociology, Politics and International Studies); Colin Nolden (Bristol Law School); and Rachel James (Geographical Sciences) were present for most of the first week and Colin was there for the full two weeks. As the Institute has observer status with the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, Alix, Rachel and Colin had the chance to engage with policy makers and climate policy experts from around the world to help promote climate action which is informed by the best evidence and research.
We asked them to give an update on their experience at COP27 and as a result, whether the pledges made at COP27 would mean that 1.5C is still achievable.
 |
| Drs Colin Nolden and Alix Dietzel at COP27. |
Climate finance – Dr Colin Nolden
Colin’s research interests span sustainable energy policy, regulation and business models and interactions with secondary markets such as carbon markets and other sectors such as mobility. COP27 was an opportunity for him to talk directly to policymakers about implementing the Paris Agreement and to people directly affected by climate policy decisions.
Here are Colin’s post-COP thoughts:
“Alongside Loss and Damage, the main issue discussed at COP is climate finance for decarbonisation. The $100bn/yr pledged in Paris has never materialised and to add injury to insult, rich countries can borrow at 4%, whereas poor countries borrow at 14%, as Mia Motley, Prime Minister of Barbados, pointed out in her speech on Day 1. Under these conditions, investments in fossil fuel infrastructures pay off, but investments in renewables do not. An endless number of panel discussions and side events on ‘climate finance’ and ‘accelerating the clean energy/net zero transition’ are testament to this gap.
“Article 6 of the Paris Agreement is a mechanism to overcome this funding gap by providing the legal foundation to finance decarbonisation projects in a country in exchange for carbon credits provided by another. Whether these should lead to according adjustments in emissions inventories, as is the case under bilateral agreements using Article 6.2, is controversial. How Article 6.4 will deal with this issue is still unclear and is unlikely to be agreed on at successive COPs. Negotiations on Article 6 will determine the climate credit and finance architecture for years to come.”
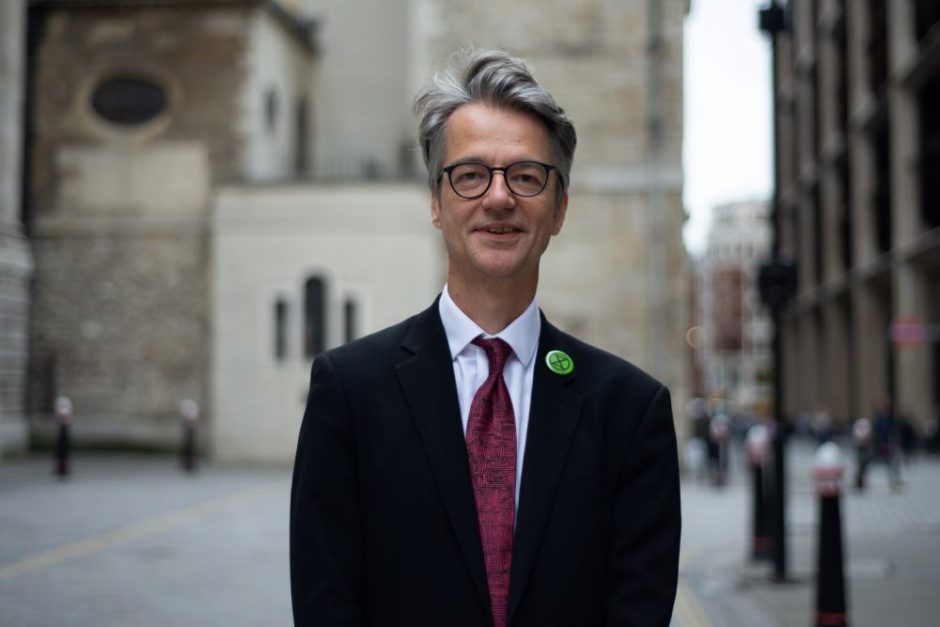
Climate justice – Dr Alix Dietzel
Alix is Associate Director for Impact and Innovation at the Cabot Institute for the Environment and an environmental justice scholar. Her role at COP27 was to observe the negotiations and critically reflect on whose voices were heard and whose were left out of the discussion, as well as concentrating on whether topics such as Loss and Damage and just transition were being given adequate space and time during the negotiations.
 |
| Dr Alix Dietzel at COP27. |
Here are Alix’s reflections from COP27:
“Despite much excitement over a new Loss and Damage fund, there is backsliding on commitments to lower emissions and phasing out fossil fuels. As an academic expert in just transition who went along this year hoping to make a difference, I share the anger felt around the world about this outcome.
“Attendance at COPs is strictly regulated. Parties (negotiating teams), the media, and observers (NGOs, IGOs, and UN Agencies) must all be pre-approved. Observers have access to the main plenaries and ceremonies, the pavilion exhibition spaces, and side-events. The negotiation rooms, however, are largely off limits. Most of the day is spent listening to speeches, networking, and asking questions at side-events. The main role of observers, then, is to apply indirect pressure on negotiators, report on what is happening, and network. Meaningful impact on and participation in negotiations seemed out of reach for many of the passionate people I met.
“It has long been known that who gets a say in climate change governance is skewed. As someone working on fair decision making as part of just transition, it is clear that only the most powerful voices are reflected in treaties such as the Paris Agreement. Despite being advertised as ‘Africa’s COP’, COP27 has further hampered inclusion. The run up was dogged by accusations of inflated hotel prices and concerns over surveillance, no chance to organize protests, and warnings about Egypt’s brutal police state.
“Arriving in Sharm El Sheik, there was an air of intimidation starting at the airport, where military personnel scrutinized passports. Police roadblocks featured heavily on our way to the hotel, and military officials surrounded the COP venue the next morning. Inside the venue, there were rumours we were being watched and observers were urged not to download the official app. More minor issues included voices literally not being heard due to unreliable microphones and the constant drone of airplanes overhead. Food queues were huge, and it was difficult to access water to refill our bottles. Sponsored by Coca Cola, we could buy soft drinks. Outside of COP, unless I was accompanied by a man, I faced near constant sexual harassment, hampering my ability to come and go freely.
“Who was there and who was most represented at COP27 also concerned me. The United Arab Emirates (UAE) registered the largest party delegation with more than 1,000 people, almost twice the size of the next biggest delegation, Brazil. Oil and gas lobby representatives were registered in the national delegations of 29 different countries and were larger than any single national delegation (outside of the UAE). At least 636 of those attending were lobbyists for the fossil-fuel industry. Despite the promise that COP27 would foreground African interests, the fossil lobby outnumbers any delegation from Africa. These numbers give a sense of who has power and say at these negotiations, and who does not.
“All this to say, I am not surprised at the outcomes. There is some good news in the form of a new fund for Loss and Damage – but there is no agreement yet on how much money should be paid in, by whom, and on what basis. More worryingly, the outcome document makes no mention of phasing out fossil fuels, and scant reference to the 1.5C target. Laurence Tubiana, one of the architects of the Paris Agreement, blamed the host country, Egypt, for the final decision.
“COP27 produced a text that clearly protects oil and gas petro-states and the fossil fuel industry. The final outcomes demonstrate that despite the thousands who were there to advocate for climate justice, it was the fossil fuel lobby who had most influence. As a climate justice scholar, I am deeply worried about the processes at COPs, especially given next year’s destination: The United Arab Emirates. Time is running out and watered-down commitments on emissions are at this stage deeply unjust and frankly dangerous.”
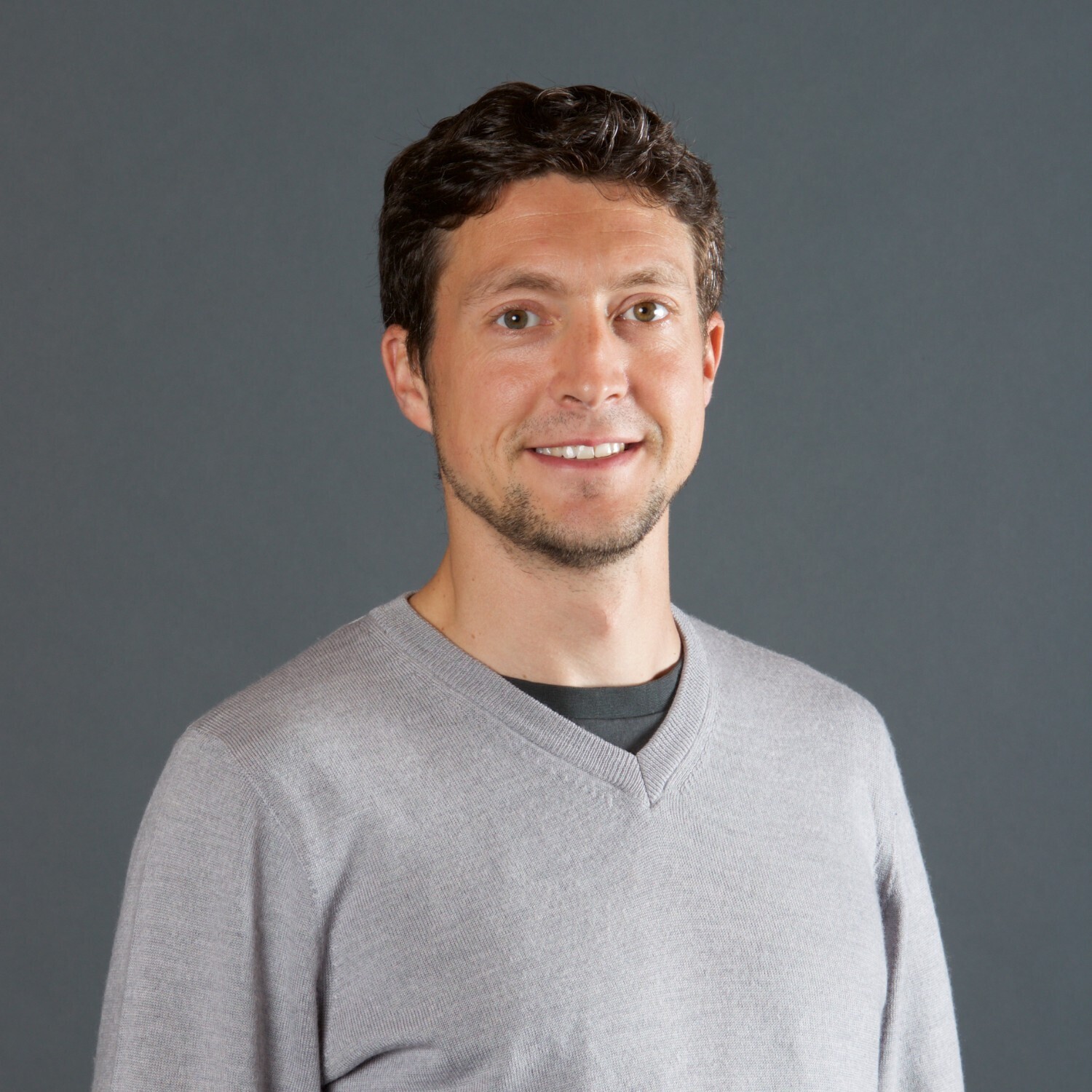
Loss and Damage – Dr Rachel James
Rachel is a climate scientist, focusing on African climate systems and developing climate science to inform and advance climate change policy. Her previous research has been designed to progress international climate policy discussions, including the COP process, and she has analysed the impacts of global mitigation goals, comparing different warming scenarios (1.5°C, 2°C and beyond). At COP27, she engaged in adaptation discussions, to learn more about how science can support national adaptation planning, to guide her new research programme “Salient”, a UKRI Future Leaders Fellowship to improve climate information for adaptation, primarily in southern Africa.
 |
| Dr Rachel James (fourth from right) at COP27. |
In her previous work, Dr James has also looked at how science can support policy discussions about ‘Loss and Damage’, from climate change, and at COP27 she followed discussions on Loss and Damage, as well as taking part in a workshop to establish a network of African researchers focusing on Loss and Damage. Rachel reflects on her experience of COP and the Loss and Damage discussions:
“The COP is now a huge event, with hundreds of discussions happening simultaneously, and many thousands of people, (almost) all pushing for climate action, and acting on it in their own ways. There are lots of things going on, deals being struck, collaborations forming, alongside the official UNFCCC business.
“This was supposed to be the “COP of implementation”, as the Paris Agreement and the rulebook are already in place. Some said we were largely beyond negotiation.
“However, the Global South came ready to negotiate, particularly on Loss and Damage. They wanted a finance facility on Loss and Damage to be established. Negotiations began in the weekend before the COP, and – after negotiating all night with no food – the developing countries succeeded in getting this onto the formal agenda.
“Over the two weeks of the COP, my perception was that there was a huge shift on Loss and Damage. Once it was on the official agenda, it was much easier to talk about. It has been a very contentious issue. Broadly, the most vulnerable countries have called for mechanisms to address the fact that they are, and will continue to, experience loss and damage from climate change impacts like sea level rise and extreme weather. Those countries who have emitted the most fear this could lead to unlimited liability. When I first started working on it I’d often get a worried look when I mentioned the topic.
“In a side event during the first week at Sharm El Sheikh, I heard someone say “some magic has happened” and we can now talk about this in the mainstream. We also saw a series of announcements from countries committing finance for Loss and Damage. Then, finally, after two weeks of negotiations ran into extra time, countries agreed to establish a fund for Loss and Damage.
“This was a huge victory for the developing countries. Lots of questions remain about how it will work, who will pay into it, and who will benefit, but nevertheless it marks a big step. Developing countries (especially AOSIS, the Alliance of Small Island States) have been working on this for decades. The negotiators work so hard, often into the night, it’s incredible.
“My overall view is that COP continues to be a difficult process, but it is shifting, maybe substantially. Many view COP as a talk shop and suggest it’s a waste of time, but I disagree. Although the process is tortuous, slow, and frustrating, it is the best one we have, and still vital. Progress is way too slow but there is progress. Every country is represented, and we don’t have any other process on climate change where that is the case. The developing countries have power in numbers at the COP that I am not sure they have in any other forum on climate change.”
 |
| Dr Alix Dietzel (fourth from right on the back row) at COP27 |
Is 1.5C still alive?
Colin: “The International Energy Agency expects fossil fuel demand to peak as early as 2025. However, with all countries harbouring exploitable fossil fuel resources racing to extract them (with our former Secretary of State for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy Rees-Mogg vowing in September 2022 to “squeeze every last drop of oil” out of the North Sea) and key initiatives such as the Glasgow Financial Alliance for Net Zero failing to deliver on their promises, fossil fuels will not be phased out anytime soon.
“At the same time, pinning our hopes on Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is misguided as current capacities amount to four hours of global emissions and International Energy Agency projections suggest that capacities in 2030 will amount to 16 hours of emissions. This implies that in the absence of a sustained global financial commitment towards demand reduction or sustainable supply, limiting average global temperature rise to 1.5 above will be very difficult indeed.”
Rachel: “A key goal in Glasgow and in Sharm El Sheikh has been to keep 1.5°C alive. Some countries were attempting to backslide on mitigation goals during the final days, but in the end 1.5°C remained in the text. It’s disappointing that we didn’t see an increase in ambition from Glasgow, but 1.5°C is still there – even if “on life support”, as noted by Alok Sharma.
“It’s easy for us to do an academic analysis and speculate as to whether or not we think 1.5°C is politically feasible. But the IPCC has spelled it out clearly: every fraction of a degree of warming matters. What’s important is that we increase ambition to reduce emissions, and we phase out fossil fuels, so that we can limit global warming as much as possible.”
———————————-
This blog is written by Cabot Institute for the Environment members Dr Alix Dietzel, Dr Colin Nolden, Dr Rachel James and Amanda Woodman-Hardy.
Further reading
Read more about our experts at COP27.
Read Dr Alix Dietzel’s blog on COP27: how the fossil fuel lobby crowded out calls for climate justice
Read Dr Colin Nolden’s blog on After COP27: Is 1.5C still alive?