Pavel V.Khon/SHutterstock
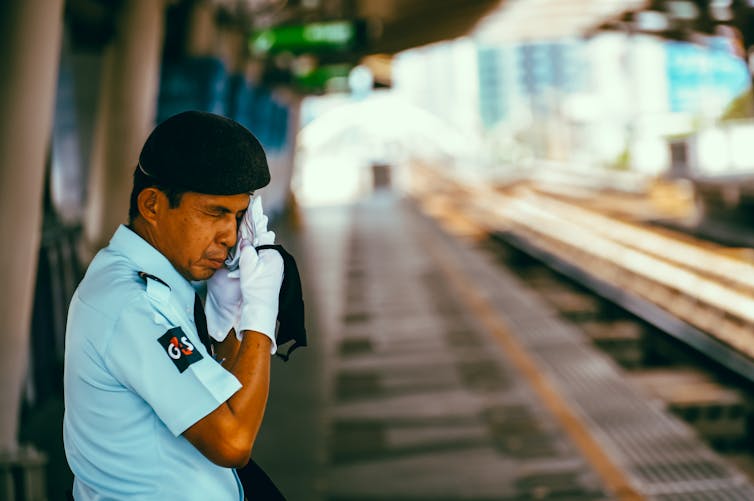
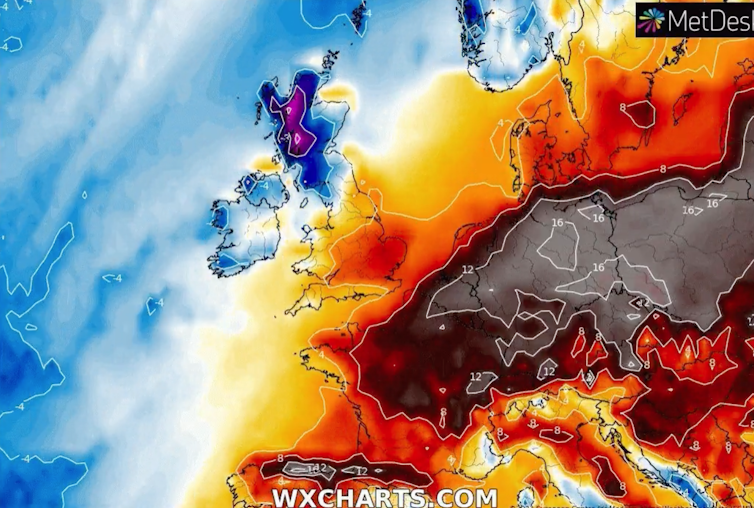
This year, even before the northern hemisphere hot season began, temperature records were being shattered. Spain for instance saw temperatures in April (38.8°C) that would be out of the ordinary even at the peak of summer. South and south-east Asia in particular were hammered by a very persistent heatwave, and all-time record temperatures were experienced in countries such as Vietnam and Thailand (44°C and 45°C respectively). In Singapore, the more modest record was also broken, as temperatures hit 37°C. And in China, Shanghai just recorded its highest May temperature for over a century at 36.7°C.
We know that climate change makes these temperatures more likely, but also that heatwaves of similar magnitudes can have very different impacts depending on factors like humidity or how prepared an area is for extreme heat. So, how does a humid country like Vietnam cope with a 44°C heatwave, and how does it compare with dry heat, or a less hot heatwave in even-more-humid Singapore?
Weather and physiology
The recent heatwave in south-east Asia may well be remembered for its level of heat-induced stress on the body. Heat stress is mostly caused by temperature, but other weather-related factors such as humidity, radiation and wind are also important.
Our bodies gain heat from the air around us, from the sun, or from our own internal processes such as digestion and exercise. In response to this, our bodies must lose some heat. Some of this we lose directly to the air around us and some through breathing. But most heat is lost through sweating, as when the sweat on the surface of our skin evaporates it takes in energy from our skin and the air around us in the form of latent heat.
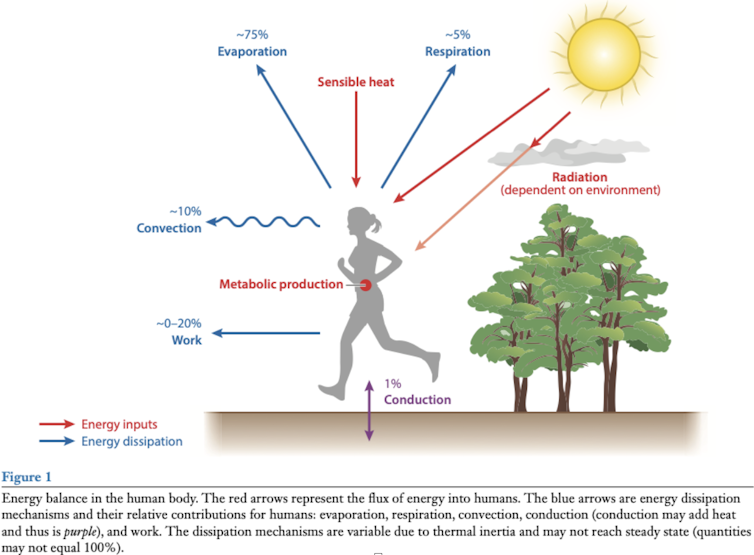
Take from Buzan and Huber (2020) Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Author provided
Meteorological factors affect all this. For example, being deprived of shade exposes the body to heat from direct sunlight, while higher humidity means that the rate of evaporation from our skin will decrease.
It’s this humidity that meant the recent heatwave in south-east Asia was so dangerous, as it’s already an extremely humid part of the world.
The limit of heat stress
Underlying health conditions and other personal circumstances can lead to some people being more vulnerable to heat stress. Yet heat stress can reach a limit above which all humans, even those who are not obviously vulnerable to heat risk – that is, people who are fit, healthy and well acclimatised – simply cannot survive even at a moderate level of exertion.
One way to assess heat stress is the so-called Wet Bulb Globe Temperature. In full sun conditions, that is approximately equivalent to 39°C in temperature combined with 50% relative humidity. This limit will likely have been exceeded in some places in the recent heatwave across south-east Asia.
In less humid places far from the tropics, the humidity and thus the wet bulb temperature and danger will be much lower. Spain’s heatwave in April with maximum temperatures of 38.8°C had WBGT values of “only” around 30°C, the 2022 heatwave in the UK, when temperatures exceeded 40°C, had a humidity of less than 20% and WBGT values of around 32°C.
Two of us (Eunice and Dann) were part of a team who recently used climate data to map heat stress around the world. The research highlighted regions most at risk of exceeding these thresholds, with literal hotspots including India and Pakistan, south-east Asia, the Arabian peninsula, equatorial Africa, equatorial South America and Australia. In these regions, heat stress thresholds are exceeded with increased frequency with greater global warming.
In reality, most people are already vulnerable well below the survivability thresholds, which is why we can see large death tolls in significantly cooler heat waves. Furthermore, these global analyses often do not capture some very localised extremes caused by microclimate processes. For example a certain neighbourhood in a city might trap heat more efficiently than its surroundings, or might be ventilated by a cool sea breeze, or be in the “rain shadow” of a local hill, making it less humid.
Variability and acclimatisation
The tropics typically have less variable temperatures. For example, Singapore sits almost on the equator and its daily maximum is about 32°C year round, while a typical maximum in London in mid summer is just 24°C. Yet London has a higher record temperature (40°C vs 37°C in Singapore).
Given that regions such as south-east Asia consistently have high heat stress already, perhaps that suggests that people will be well acclimatised to deal with heat. Initial reporting suggests the intense heat stress of the recent heatwave lead to surprisingly few direct deaths – but accurate reporting of deaths from indirect causes is not yet available.
On the other hand, due to the relative stability in year-round warmth, perhaps there is less preparedness for the large swings in temperature associated with the recent heatwave. Given that it is not unreasonable, even in the absence of climate change, that natural weather variability can produce significant heatwaves that break local records by several degrees Celsius, even nearing a physiological limit might be a very risky line to tread.
—————————–
This blog is written by Cabot Institute for the Environment members: Dr Alan Thomas Kennedy-Asser, Research Associate in Climate Science; Professor Dann Mitchell, Professor of Climate Science, and Dr Eunice Lo, Research Fellow in Climate Change and Health, University of Bristol. This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.